Document Type
Article
Publication Date
2020
DOI
doi.org/10.1002/dneu.22801
Creative Commons License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Description
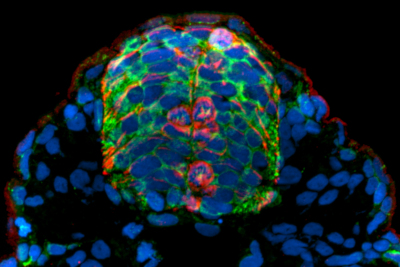
During embryonic development of bilateral organisms, neurons send axons across the midline at specific points to connect the two halves of the nervous system with a commissure. Little is known about the cells at the midline that facilitate this tightly regulated process. We exploit the con served process of vertebrate embryonic development in the zebrafish model system to elucidate the identity of cells at the midline that may facilitate postoptic (POC) and anterior commissure (AC) development. We have discovered that three differentgfap+ astroglial cell morphologies persist in contact with pathfinding axons throughout commissure formation. Similarly, olig2+ progenitor cells occupy delineated portions of the postoptic and anterior commissures. These early olig2+ progenitors demonstrate glial-like morphologies despite the lack of a myelination marker. Moreover, we conclude that both the gfap+ and olig2+ progenitor cells give rise to neuronal populations in both the telencephalon and diencephalon. Interestingly, these varied cell populations showed significant developmental heterochrony between the telencephalon and diencephalon. Lastly, we also showed that fli1a+ mesenchymal cells migrate along the presumptive commissure regions before and during midline axon crossing. Furthermore, following commissure maturation, specific blood vessels formed at the midline of the POC and immediately ventral and parallel to the AC. This comprehensive account of the cellular populations that correlate with the timing and position of commissural axon pathfinding has supported the conceptual modeling and identification of the early forebrain architecture that may be necessary for proper commissure development.
Recommended Citation
Schnabl, Jake; Litz, M.P.H; Schneider, Caitlin; PenkoffLidbeck, N.; Bashiruddin, Sarah; Schwartz, M. S.; Alligood, Kristin; and Barresi, Michael, "Characterizing the Diverse Cells that Associate with the Developing Commissures of the Zebrafish Forebrain" (2020). Article, Smith College, Northampton, MA.
https://scholarworks.smith.edu/bl_zfcc/33


Comments
Published in Developmental Neurobiology
Peer reviewed accepted manuscript.